On November 23, 2021, the Indiana Department of Health updated COVID-19 clinical guidance and toolkit to complement the most recent CMS guidance related to visitation for Nursing Homes and Assisted Living.
The updates are noted below in red text.
The COVID-19 Clinical Guidance restates prior guidance in the areas of guiding principles, the prevention of introduction of COVID-19 into a facility, exposure definitions, treatment for symptomatic individuals, protocol for known COVID-19 cases (both residents and heath care personnel/return to work), staffing shortage protocols, resident assessment, new admission and re-admissions, outbreaks, reporting requirements, residents leaving the facility, and testing.
It is critical that facilities read this guidance and compare it to current facility policies. Much of what is contained in this COVID-19 Clinical Guidance is restatement of existing best practice.
Key reminders and areas:
Guiding Principles
- Adds the practice of discussing with the resident’s physician or specialist to determine whether a resident is immunocompromised.
Key Indicators
- Adds discussion of community transmission, which refers to the level of COVID-19 transmission in the county where the facility is located. Community transmission, and not solely positivity rate, is now the standard by which routine testing is determined for purposes of the routine testing requirements in CMS’s QSO 20-38.
Screening
- Indicates screening can be done by an electronic monitoring system, in addition to by an individual, when the electronic monitoring system permits an individual to self-report before entering a facility.
Exposure
- HCP wearing proper PPE caring for a known COVID-19 case is not considered an exposure.
- Antigen Test Interpretation/Algorithm
- Unvaccinated staff with exposure excluded from work for 14 days, testing at two days, and if negative again at day 5-7
- Vaccinated staff with high-risk exposure undergo testing at two days, and if negative again and at day 5-7 and do not need to be excluded from work when asymptomatic. They must use universal source control while in the facility for 14 days from exposure.
- Vaccinated staff with exposure (not high risk) testing at days 5-7 and do not need to be excluded from work when asymptomatic.
- HCP with COVID-19 in the past 90 days do not need to be restricted from work due to high-risk exposure if asymptomatic. They must use universal source control while in the facility for 14 days from exposure.
- Increase monitoring of residents with exposure with symptom assessment, vital signs, oxygen saturation, and respiratory exams to identify and managed serious infection.
- Residents with close contact should be tested at two days from exposure, and if negative should be tested again at 5-7 days after exposure.
- Asymptomatic residents with close contact do not need to be tested or put in TBP if they had a confirmed COVID-19 infection in the last 90 days.
- Fully vaccinated residents with close contact do not need to be in TBP if asymptomatic unless they are moderately to severely immunocompromised.
- Unvaccinated residents with known exposure to COVID-19 should be monitored in yellow zone TBP for the full 14 days. Testing negative does not warrant movement back to green zone until 14 days have passed
Symptomatic Individuals
- Treated the same irrespective of vaccination status. Residents placed in TBP. Staff should be tested, restricted from work until isolation period is complete or alternative diagnosis confirmed.
- Consider testing for pathogens other than COVID-19 and initiating appropriate infection prevention precautions for symptomatic older adults. See CDC Interim Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations.
Known COVID-19 Cases
- Residents in red zone for 10 days when mild/moderate; in red zone for 20 days with severe/immunocompromised.
- Assess 3x daily and discusses treatment options with medical director (monoclonal antibody therapy should be considered)
- Increase monitoring of residents with exposure with symptom assessment, vital signs, oxygen saturation, and respiratory exams to identify and managed serious infection.
- Heath Care Personnel isolate at home and follow CDC return to work criteria
- In case of staffing shortage, the facilities with active COVID-19 cases can continue to allow asymptomatic COVID-positive HCP to work in the COVID-19 unit (red zone) of the facility.
Staffing Shortages
- Refer to CDC Staff Shortage Mitigation Strategies that permit asymptomatic high-exposed HCPs to return to work earlier with additional daily screening and reporting.
- Determine Crisis capacity strategy implementation.
- If staffing shortages persist beyond implementation of mitigation, as a last resort HCPs with suspected or confirmed cases and are well enough/willing to work can work under certain circumstances.
- When possible, HCPs working the Red Unit should be dedicated. If this is not possible, use the following guidance:
- Assure that red and yellow zone is clearly marked and each resident’s door has TBP signage for proper PPE.
- Recommend using conventional PPE for all staff who cross zones during their shift. See the guidance in COVID-19 Infection Control Guidance in Long Term Care Facilities section of SOP.
- Staff may be shared in the red and yellow zone as your first mitigation, working from yellow zone to red zone.
- If using the same staff for both green and red zone, perform frequent infection control rounds to assure proper PPE donning, doffing and hand hygiene. Working from green zone, then yellow then red zone.
- Consider staffing with vaccination status of your team in mind.
- Assure full cohorting of equipment and supplies per zone.
- Refer to Crisis Capacity Staffing from CDC
New Admissions and Readmissions
- If the resident or family member reports possible close contact with an individual with COVID-19 while outside of the nursing home, test the resident for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status. A nursing home may also opt to test unvaccinated residents without signs or symptoms if they leave the nursing home frequently or for a prolonged length of time, such as over 24 hours.
- Residents that are outside of the facility for more then 24 hours are a readmission.
- All new admissions and readmissions must be screened and treated according to screening results.
- Unvaccinated new admissions and readmissions should be placed in TBP even if they have a negative test.
- Full vaccinated new admissions and readmissions do not need to be in TBP if asymptomatic and pass screening protocol. If any prolonged contact with a known positive or symptom is present, then the fully vaccinated resident should be treated according to exposure protocol.
- All new admissions should be given a POC test. If positive, follow up with PCR and resident place in yellow zone until PCR results returned. Resident moved to red zone if positive confirmed by PCR.
- Residents with confirmed COVID-19 in the last 90 days do not need to be in TBP due to new admission or re-admission. They do not need to be tested if asymptomatic due to new admission or re-admission.
- All readmissions should be monitored for symptoms and POC test may be considered at 3-5 days based on screening or high-risk activities.
- Facilities should not require a hospital to test a patient for COVID-19 before discharge if there is no clinical indication to test.
Outbreaks
Outbreak is defined as a single staff case or any single facility onset resident case.
- During outbreak consider increasing monitoring of all residents from daily to every shift, to detect new symptoms more rapidly.
- Exclude testing for those with previous COVID-19 infection in the last 90 days, unless symptomatic.
- If healthcare associated transmission is suspected, consider expanded testing of HCP and residents. Distribution and number of cases and the ability to identify close contacts to be considered.
There are two options for outbreak testing:
Option 1:
Facility can conduct contract tracing and identify close contacts of the individual with COVID-19, it could choose to conduct focused testing based on known close contacts.
- If testing of close contacts reveals additional HCP or residents with SARS-COV-2 infection, contact tracing for those individuals to be continued to identify other resident and or HCW close contacts. This includes HCP with higher risk exposures to the newly identified individuals with COVID-19 infection.
- When contact tracing resources are limited, option 2 below – facility wide or group level testing to be considered.
- Option 2 – facility wide or group level testing to be considered if contact tracing fails to halt transmission.
Option 2:
Facility does not have resources to identify close contacts, a facility-wide or group-level (e.g., unity, floor, or other specific area(s) of the facility).
- Unvaccinated residents and HCP:
- Unvaccinated residents should generally be restricted to their rooms, even if testing is negative.
- HCP to wear N95 or higher respirator, eye protection (goggles and an appropriate face shield that covers the front and sides of the face), gloves and gown.
- Group activities to be suspended.
- Identified close contacts should be managed as described in Exposure section.
- Fully Vaccinated residents and HCP:
- Fully vaccinated residents to be tested
- Do not need to be restricted to their rooms or cared for by HCP using the full PPE recommended for the care of a resident with COVID-19 unless symptoms develop and or tested and positive with COVID-19.
- For guidance about work restriction for fully vaccinated HCP who have higher-risk exposures, refer to Interim U.S. Guidance for Managing Healthcare Personnel with SARSCoV-2 infection or Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (CDC 9.10.21).
- When transmission within a facility is not controlled with initial interventions, considerations to use of quarantine for fully vaccinated residents and work restriction of fully vaccinated HCP with higher-risk exposures.
- No additional cases identified, room restriction and full PPE used by HCP caring for unvaccinated residents can be discontinued after 14 days and no further testing is indicated.
- If additional cases are identified, testing should continue affected units or facility-wide every 3-7 days in addition to room restriction and full PPE use for care of unvaccinated residents, until no new cases for 14 days.
- If antigen testing is used, more frequent testing (every 3 days) to be considered.
Refusal to test:
If outbreak testing has been triggered and an unvaccinated staff member refuses testing:
- Restrict the staff member from the building until the procedures for outbreak testing have been completed.
- Follow occupational health and local jurisdiction policies with respect to any asymptomatic unvaccinated staff who refuse testing.
If outbreak testing has been triggered and an asymptomatic resident refuses testing:
- The facility should be vigilant and monitor to ensure the resident maintains appropriate distance from other residents, wears a face covering, and practices effective hand hygiene.
- Residents who refuse testing may require TBP based on symptoms or vaccination status.
- Reminder that outbreak testing is not triggered when a staff member has a community-acquired case (exposed outside of the facility and was not in the facility while potentially infectious).
Reporting
- No change. Reminder to report all cases and deaths within 24 hours per Data Submission Guidelines
Residents Leaving the Facility
- Residents who leave the facility for 24 hours or longer to be managed as a readmission.
- Residents may leave the facility as they choose.
- Facilities to remind resident and any individuals accompanying the resident to adhere to the core principles of infection control while outside the facility (face mask, physical distancing, and hand hygiene).
- Screen each resident for signs, symptoms and/or exposure to COVID-19 upon return from each excursion and follow guidance under symptomatic individuals and or exposure.
- Facilities may test unvaccinated residents without signs or symptoms if they leave the nursing home frequently or for a prolonged period.
- Facilities may consider quarantining unvaccinated resident who leave the facility if an assessment of risk is apparent, or uncertainty exits about their adherence or the adherence of those around them to recommended infection prevention.
- Residents that leave for routine and/or frequent medical appointments for fewer than 24 hours must be screened upon return. Quarantine is not recommended when the resident does not have close contact with a known positive. Testing upon return from a medical appointment is not required – follow screening protocol.
- Residents should observe core principles of infection control while outside of the facility
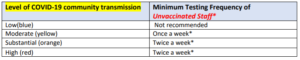
Routine Staff Testing
- Routine testing of staff now depends on level of COVID-19 community transmission, and not just on county positivity rates, per CMS QSO 20-38, updated 9/10/2021.
- Vaccinated staff do not need to be routinely tested (unless symptomatic)
- The facility should test all unvaccinated staff at the frequency prescribed in the Routine Testing table based on the level of community transmission reported in the past week. Facilities should monitor its level of community transmission every other week (e.g., first and third Monday of every month) and adjust the frequency of performing staff testing according to the table.
- If the level of community transmission increases to a higher level of activity, the facility should begin testing staff at the frequency shown in the table above as soon as the criteria for the higher activity level are met.
- If the level of community transmission decreases to a lower level of activity, the facility should continue testing staff at the higher frequency level until the level of community transmission has remained at the lower activity level for at least two weeks before reducing testing frequency.